In general, a project can be interpreted as follows: Project is an endeavor that is limited by time (temporary) by using a limited number of resources to produce a unique product or service.
According to PMBOK, the project can be interpreted as follows:
“A project is a temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result.“
The keywords that need more attention in the above project understanding are temporary and unique.
Each project must have a milestone start and milestone finish and must deliver unique products, services, or results.
As a simple illustration, a leader of an educational institution makes the statement “We want to increase our student’s passing score with an average score of 9” cannot be qualified as a project. However, if the statement is as follows: “We want to increase the average value of our students to 9 in the next 3 years” can be qualified as a project.
Another illustration if someone states “I want to raise as much as USD 50000” cannot be indicated as a project. But if someone states “I want to raise as much as USD 50000 within the next 5 years” it might be qualified as a project.
Besides the projects you find at the office, some of the things you have planned and worked on outside of the office may also be projects. The following list is an example of a commercial or personal project that you may have worked on:
- Construct a flyover.
- Landscape the backyard.
- Obtain financial aid for your college education.
- Launch a new advertising campaign.
- Move into a new office.
- Discover a new herbal and bring it to market.
- Build a retirement portfolio.
- Migrate corporate data to a new server farm.
- Throw your husband a surprise fortieth birthday party.
- Produce a marketing brochure for new services.
Also, read the What is free float, total float and lag in CPM, RACI Matrix; 5Ws+1h in Project Management.
What is the difference between Program and Project

In Project Management, a program can be defined as a group of projects or services that are interrelated for a particular purpose which is usually managed by an organization or a particular entity.
So, in one program can consist of several projects that are interrelated.
Project Management
“Project management is the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet the project requirements. Project management is accomplished through the appropriate application and integration of the project management processes identified for the project. Project management enables organizations to execute projects effectively and efficiently.” ~ PMBOK
Project Management can be interpreted as the application of methods, knowledge, best skills with limited resources to achieve predetermined goals, in order to obtain optimal results in terms of cost performance, quality and time, and work safety.
A project can run with or without management. But even though it can run without management, a project that is not well managed will easily end up halfway or very little to be completed (run to the end).
In general, project management should be able to answer the following questions:
What problems are you solving?
One of the project management functions is to identify problems that must be solved and resolved by the project.
Most people immediately provide solutions before identifying problems that exist or might occur at a later date.
Dr. Joseph M. J., a well-known project management consultant, said that a project is scheduling problems to reach a solution.
To answer the questions above, before you provide a solution, you need to identify the problem first.
Identify what problem you have, what the main problem is, and what the real problem is. After the problem can be identified, you can provide step-by-step and scheduled solution steps.
How are you going to solve it?
After the problem has been identified, the following question that needs to be answered is how to solve the problem. You need to make plans such as how long it will take, how much it will cost, how many workers will be involved, and others.
How will you know when you’re done?
To answer the questions above, you need to define what goals you want to achieve on a project and what project needs you will run. You need to determine the success criteria of your project at the beginning so that you can know whether your project is successful or not.
Also, read what is S-Curve in Project Management?
How well did it go?
The project team needs to document what went well and what went wrong or was detrimental.
Everything, whether it benefits or results in losses, needs to be Lesson Learned.
Every good thing that happens needs to get a record, why it went well, and the detrimental thing that happened also needs to get a record of why it didn’t go according to plan.
Besides, it is also necessary to document how the project will be implemented in the future so that good thing can be continued or improved while the harmful things can be avoided.
The approach in Project Management

Reporting from Wrike, there are two main approaches to project management, as below:
Traditional
The traditional approach tends to be essential to some industries, such as manufacturing.
Usually, industries that use this approach produce physical products such as cars, computers, buildings, or other products.
- Waterfall
When using this approach, each task in the project must be completed one by one before starting the next task.
- Critical path method
This method is more or less the same as Waterfall, using a sequential approach.
The project manager can prioritize the resources needed, as well as other more important tasks or jobs to do first.
Any other work that might hinder the project’s progress will be carried out last.
- Critical chain project management (CCPM)
CCPM focuses on the resources required for each task and work in the project.
The project manager will identify the tasks with the highest priority, then create a schedule around those priorities.
This is done to ensure that the main focus of the project can be realized.
Agile
The agile approach to project management focuses on team collaboration rather than hierarchical structures.
This approach was developed for software development in 2001.
- Scrum
In contrast to the traditional approach, the Scrum approach allows team members to have the burden of responsibilities that the project manager usually carries.
The Scrum Master holds the position of leader and facilitator in this approach.
- Kanban
The Kanban approach is more or less the same as Scrum, but with a more continuous work period.
- Extreme programming (XP)
Well, the XP approach was developed specifically for software engineering.
This approach is suitable for projects with clients who do not yet know what the final result will require.
This is because using XP; the project manager can experiment and provide feedback to clients.
- Adaptive project framework (APF)
The APF approach is also suitable for technology and information-based projects that require flexibility and a high degree of adaptation.
Project Management Process
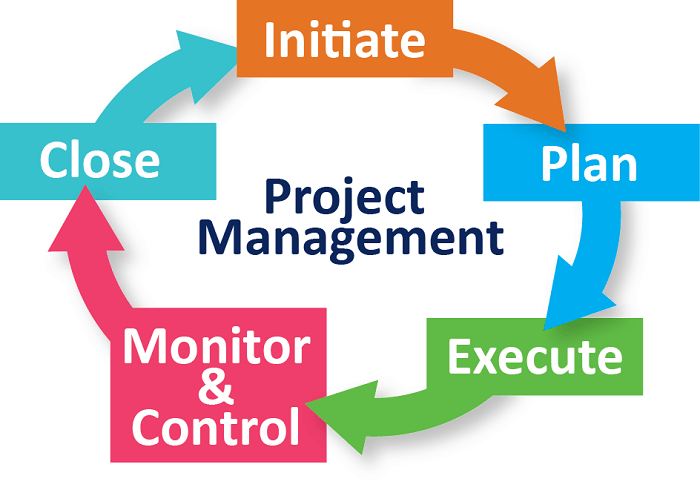
It can be explained that the project management process starts from the project definition, initiation, planning, execution to control based on project goals (objectives), costs, information used, resources, time, and needs that are adjusted to the development of time.
According to PMBOK project management is divided into five process groups, namely:
Initiating
The initiation phase is a sign of commitment to starting the project.
In this phase, the project manager and team explore the true goals of the project, identify potential project stakeholders, and work with customers and other stakeholders to produce approaches to achieve project goals.
In the Initiation phase, a project is held to answer the question, “What problem are you solving?” In this phase, the project manager and team prepare a summary of the project and its business benefits.
The initiation phase is complete when management gives the approval to move to the planning stage.
Planning
At the planning stage, the project manager and teamwork in detail on how the problem will be resolved.
During the planning phase, the project manager and the team identify in detail what work needs to be done, who will do it, how to do it, the costs involved, how long, when it will be done, etc.
The hope is that the project can be implemented with the desired quality level at the cost, number of workers, and the desired duration of time.
Executing
Project implementation is the implementation or continuation of planning. In this phase, the first step taken is launching the project. The project organization (project manager and team) will be defined along with all the rules.
You and the project team will carry out the project concerning the employer’s requirements and their rules and focus on achieving the target of the project.
Controlling
The project manager and team will exercise control over the project by monitoring the work and focusing on project performance, whether the project is on track as planned or there are changes.
If an inevitable change of plans occurs, problems or disasters occasionally arise, the project manager and team will need to define a corrective plan to get the project back on track.
Closing
The project is closed if it meets the criteria for completion of the employer and is in accordance with the contract. The closing also includes completing a document containing the final progress of the work, handing over the work, and the final report, including lessons-learned when building the project.
Prior to project closure, all forms of obligations and administration between the employer and the contractor have been completed and have received official written agreement.
Aspects of Project Management
Financial Aspect: This aspect is related to project financing. Usually, this aspect comes from own costs, investors, or loans in the short, medium, or long term. Project financing is crucial that requires careful financial analysis and planning.
Budget Aspect: This aspect relates to planning and controlling costs throughout the project. Careful planning will facilitate the cost control process to fit the budget plan. Conversely, if planning is wrong there will be an increase in the budget that can harm the project owner.
Human Resources Management Aspect: This aspect relates to the need for human resource allocation throughout the project. In order to be efficient, Human Resources management is based on a previously formed project organization.
Production Management Aspect: These aspects relate to the final results of the project. The end result is negative if the planning and control process is not good. For good productivity, efforts are made to improve the productivity of Human Resources, improve the efficiency of the production and work processes, and improve the production process through quality assurance and quality control.
Price Aspect: This aspect appears to avoid external conditions where the product produced requires high production costs and cannot compete with other products.
Effectiveness and Efficiency Aspect: This aspect is related to the function of the product produced as well as the efficiency factor that needs to be met so that the costs are as planned.
Marketing Aspect: This aspect is related to price competition, promotion strategies, product quality, and market analysis of the products produced.
Quality Aspect: This aspect is related to the quality of the final product that can improve competitiveness and give satisfaction to customers.
Time Aspect: Time aspects can lead to increased costs if there are delays and can be beneficial if resource productivity is high so that project completion is faster than planned.
Also read What is Agile Methodology in Project Management?
- Earned Value Method: What is it and how to use it - December 24, 2023
- What is the Critical Path Method in Project Management - November 23, 2023
- What is Free Float, Total Float, and Lag in CPM - November 19, 2023